Monitoring Stash with builtin Prometheus
This tutorial will show you how to configure builtin Prometheus scraper to monitor Stash backup and recovery operations as well as Stash operator.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube.
To keep Prometheus resources isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace to deploy Prometheus server.
$ kubectl create ns monitoring
namespace/monitoring created
Enable Monitoring in Stash
Enable Prometheus monitoring using prometheus.io/builtin agent while installing Stash. To know details about how to enable monitoring see here. Here, we are going to enable monitoring for both backup & recovery and operator metrics.
$ curl -fsSL https://github.com/stashed/installer/raw/v0.9.0-rc.0/deploy/stash.sh | bash -s -- \
--monitoring-agent=prometheus.io/builtin \
--monitoring-backup=true \
--monitoring-operator=true \
--prometheus-namespace=monitoring
This will add necessary annotations to stash-operator service. Prometheus server will scrape metrics using those annotations. Let’s check which annotations are added to the service,
$ kubectl get service -n kube-system stash-operator -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"app":"stash"},"name":"stash-operator","namespace":"kube-system"},"spec":{"ports":[{"name":"api","port":443,"targetPort":8443},{"name":"pushgateway","port":56789,"targetPort":56789}],"selector":{"app":"stash"}}}
prometheus.io/operator_path: /metrics
prometheus.io/operator_port: "8443"
prometheus.io/operator_scheme: https
prometheus.io/pushgateway_path: /metrics
prometheus.io/pushgateway_port: "56789"
prometheus.io/pushgateway_scheme: http
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
creationTimestamp: 2018-11-07T04:10:26Z
labels:
app: stash
name: stash-operator
namespace: kube-system
resourceVersion: "1649"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/stash-operator
uid: 0e73664a-e243-11e8-a768-080027767ca3
spec:
clusterIP: 10.105.200.228
ports:
- name: api
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8443
- name: pushgateway
port: 56789
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 56789
selector:
app: stash
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
Here, prometheus.io/scrape: "true" annotation indicates that Prometheus should scrape metrics for this service.
The following three annotations point to pushgateway endpoints which provides backup and recovery metrics.
prometheus.io/pushgateway_path: /metrics
prometheus.io/pushgateway_port: "56789"
prometheus.io/pushgateway_scheme: http
The following three annotations point to api endpoints which provides operator specific metrics.
prometheus.io/operator_path: /metrics
prometheus.io/operator_port: "8443"
prometheus.io/operator_scheme: https
Now, we are ready to configure our Prometheus server to scrape those metrics.
Deploy Prometheus Server
We have deployed Stash in kube-system namespace. Stash exports operator metrics via TLS secured api endpoint. So, Prometheus server need to provide certificate while scraping metrics from this endpoint. Stash has created a secret named stash-apiserver-certs with this certificate in monitoring namespace as we have specified that we are going to deploy Prometheus in that namespace through --prometheus-namespace flag. We have to mount this secret in Prometheus deployment.
Let’s check stash-apiserver-cert certificate has been created in monitoring namespace.
$ kubectl get secret -n monitoring -l=app=stash
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
stash-apiserver-cert kubernetes.io/tls 2 2m21s
Create RBAC:
If you are using a RBAC enabled cluster, you have to give necessary RBAC permissions for Prometheus. Let’s create necessary RBAC stuffs for Prometheus,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/stashed/docs/raw/v0.9.0-rc.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin/prom-rbac.yaml
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/stash-prometheus-server created
serviceaccount/stash-prometheus-server created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/stash-prometheus-server created
Create ConfigMap:
Now, create a ConfigMap with necessary scraping configuration. Bellow, the YAML of ConfigMap that we are going to create in this tutorial.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: stash-prometheus-server-conf
labels:
name: stash-prometheus-server-conf
namespace: monitoring
data:
prometheus.yml: |-
global:
scrape_interval: 30s
scrape_timeout: 10s
evaluation_interval: 30s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: stash-pushgateway
scrape_interval: 30s
scrape_timeout: 10s
metrics_path: /metrics
scheme: http
honor_labels: true
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_label_app]
regex: stash # default label for stash-operator service is "app: stash". customize this field according to label of stash-operator service of your setup.
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
regex: true
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
regex: pushgateway
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_pushgateway_path]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
action: replace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_pushgateway_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_pushgateway_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
separator: ;
regex: (.*)
target_label: namespace
replacement: $1
action: replace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
separator: ;
regex: (.*)
target_label: service
replacement: $1
action: replace
- job_name: stash-operator
scrape_interval: 30s
scrape_timeout: 10s
metrics_path: /metrics
scheme: https
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/secret/stash-apiserver-cert/tls.crt
server_name: stash-operator.kube-system.svc
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_label_app]
regex: stash # default label for stash-operator service is "app: stash". customize this field according to label of stash-operator service of your setup.
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
regex: true
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
regex: api
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_operator_path]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
action: replace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_operator_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_operator_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
separator: ;
regex: (.*)
target_label: namespace
replacement: $1
action: replace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
separator: ;
regex: (.*)
target_label: service
replacement: $1
action: replace
Here, we have two scraping job. One is stash-pushgateway that scraps backup and recovery metrics and another is stash-operator which scraps operator metrics.
Look at the tls_config field of stash-operator job. We have provided certificate file through ca_file field. This certificate comes from stash-apiserver-cert that we are going to mount in Prometheus deployment. Here, server_name is used to verify hostname. In our case, the certificate is valid for hostname server and stash-operator.kube-system.svc.
Also note that, we have provided a bearer-token file through bearer_token_file field. This file is token for stash-prometheus-server serviceaccount that we have created while creating RBAC stuffs. This is required for authorizing Prometheus to Stash API Server.
Let’s create the ConfigMap we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/stashed/docs/raw/v0.9.0-rc.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin/prom-config.yaml
configmap/stash-prometheus-server-conf created
Deploy Prometheus:
Now, we are ready to deploy Prometheus server. YAML for the deployment that we are going to create for Prometheus is shown below.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: stash-prometheus-server
namespace: monitoring
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
spec:
serviceAccountName: stash-prometheus-server
containers:
- name: prometheus
image: prom/prometheus:v2.4.3
args:
- "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml"
- "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus/"
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
volumeMounts:
- name: prometheus-config-volume
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
mountPath: /prometheus/
- name: stash-apiserver-cert
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/secret/stash-apiserver-cert
volumes:
- name: prometheus-config-volume
configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: stash-prometheus-server-conf
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
emptyDir: {}
- name: stash-apiserver-cert
secret:
defaultMode: 420
secretName: stash-apiserver-cert
items: # avoid mounting private key
- key: tls.crt
path: tls.crt
Notice that, we have mounted stash-apiserver-cert secret as a volume at /etc/prometheus/secret/stash-apiserver-cert directory.
Now, let’s create the deployment,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/stashed/docs/raw/v0.9.0-rc.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin/prom-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/stash-prometheus-server created
Verify Monitoring Metrics
Prometheus server is running on port 9090. We are going to use port forwarding to access Prometheus dashboard. Run following command on a separate terminal,
$ kubectl port-forward -n monitoring stash-prometheus-server-9ddbf79b6-8l6hk 9090
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9090 -> 9090
Forwarding from [::1]:9090 -> 9090
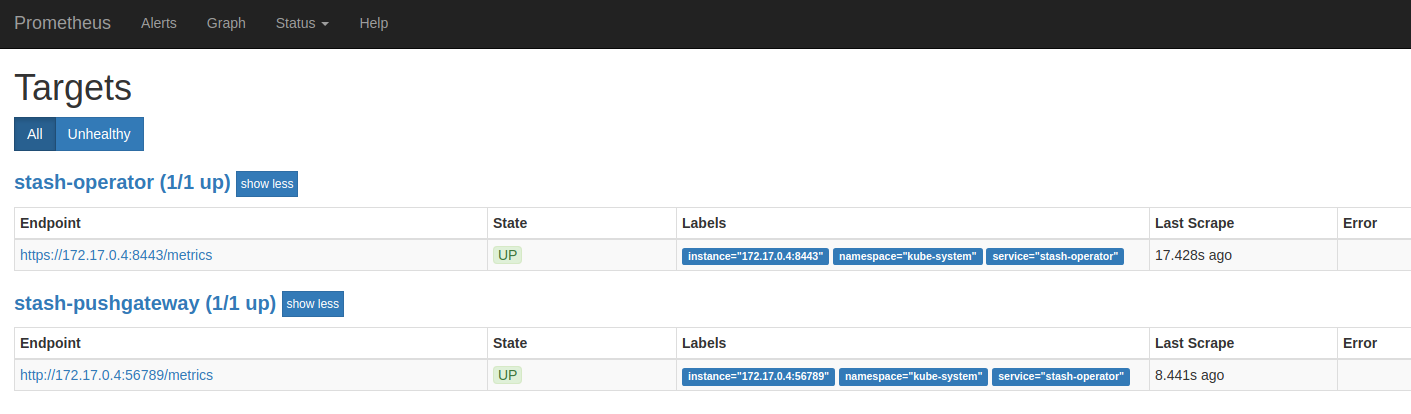
Now, we can access the dashboard at localhost:9090. Open http://localhost:9090 in your browser. You should see pushgateway and api endpoints of stash-operator service as targets.
Cleanup
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl delete clusterrole stash-prometheus-server
kubectl delete clusterrolebinding stash-prometheus-server
kubectl delete serviceaccount/stash-prometheus-server -n monitoring
kubectl delete configmap/stash-prometheus-server-conf -n monitoring
kubectl delete deployment stash-prometheus-server -n monitoring
kubectl delete secret stash-apiserver-cert -n monitoring
kubectl delete ns monitoring
To uninstall Stash follow this guide.